Acrylic glass - properties and types
Monday, June 15, 2020
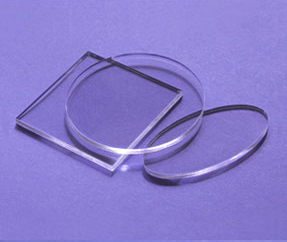 Acrylic glass (technical term: PMMA) is a glass-like plastic that impresses with its high transparency, beautiful appearance and excellent processing options.
Acrylic glass (technical term: PMMA) is a glass-like plastic that impresses with its high transparency, beautiful appearance and excellent processing options.No matter under which trade name this art glass is offered, you usually have the choice between the types GS and XT .
Cast acrylic glass (GS) : The liquefied material is poured into a mould.
Extruded acrylic glass (XT) : The viscous material is pressed through a nozzle that shapes it into the desired shape, alternatively the shaping is done by rollers.
Comparison of the acrylic glass properties
| Acrylic glass GS | Acrylic glass XT | |
| Surface quality | a little better | - |
| Durability (Age/Weather) | about the same | about the same |
| Strength | a little bigger | - |
| Optical properties | a little better | - |
| Thickness tolerance | Tolerance +/- (0.4 +0.1 x thickness). Example: thickness 4 mm, thicknesses from 3.2 to 4.8 mm are possible. | Tolerance: +/- 5% (from a panel thickness of 3 mm). Example: thickness 4 mm, thicknesses from 3.8 to 4.2 mm are possible. |
| Processing | easier | tends to melt |
| Stress cracks | - | possible |
| Price | - | cheaper |
Notes on optical properties
Acrylic glass can be obtained with various optical properties:Transparent
You will receive crystal-clear, colorless acrylic glass that is reminiscent of window glass.
Semi-transparent
There is also often talk of opal or opaque . The semi-transparent acrylic glass or frosted glass is translucent (usually less than 70%) and scatters the light. Blurred contours can be seen through the glass.Originally, the effect was created by roughening surfaces on one or both sides by sandblasting. Currently, the frosted glass can also have a glossy surface. Nevertheless, the term satin is often used as a synonym for semi-transparent.